DMI Plus
DMI Plus is an extremely powerful catalytic water filtration media that is designed for the removal of iron and manganese in water. The media displays colour from dark brown to black, in which the colour is produced by Manganese Oxide in the outer layer of the granules. DMI Plus acts as an oxidation catalyst with immediate oxidation and filtration of the insoluble precipitates.

DMI-Plus is an extremely powerful catalytic water filtration media that is designed for the removal of iron and manganese in aqueous solutions water without the need for potassium permanganate or chemical regeneration. This media displays colour from dark brown to black, in which the colour is produced by Manganese Oxide in the outer layer of the granules. DMI-Plus acts as an oxidation catalyst with immediate oxidation and filtration of the insoluble precipitates derived from this oxidation reaction
Liner Velocity for Iron & Manganese Concentrations
| Iron Concentration | Linear Velocity | Manganese Concentration | |
| 0.3 - 1.0 ppm | 15 - 20 m3/hr/m2 | - | |
| 1 - 5 ppm | 1- - 15 m3/hr/m2 | - | |
5 - 15 ppm | 7 - 10 m3/hr/m2 | 0.5 - 1 ppm | |
| > 15 ppm | 5 - 7 m3/hr/m2 | 1 -2 ppm |
DMI-Plus Physical and Chemical Characteristic
| Physical Properties | Specification | |
| Color | Brown to Black | |
| Bulk Density | 1460kg/m3 | |
| Specific Gravity | 2.69 | |
| Effective Size | 0.3 - 0.6mm | |
| Uniformity Coefficient | 1.4 | |
| pH Range | 5.8 - 8.6 | |
| Max Water Temp | 50c |
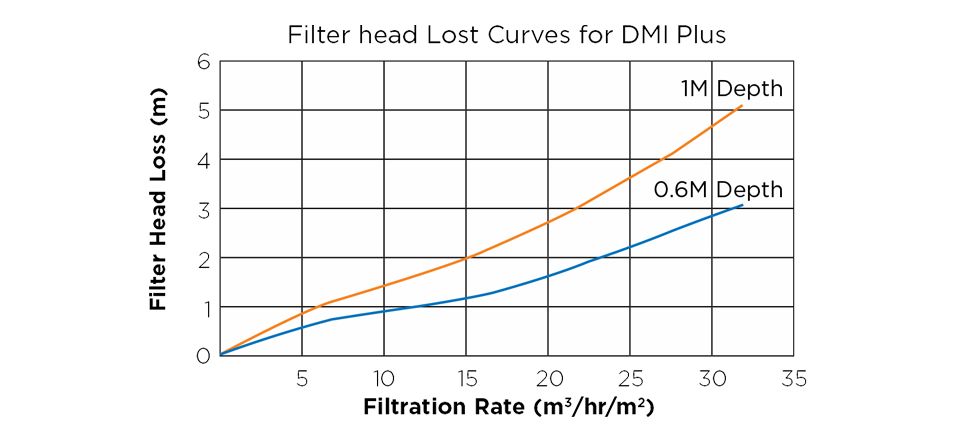
Filter head Lost Curves for DMI PLUS
The pressure drop correlates with the water velocity through the filter and media depth. The chart below shows pressure drop with different media bed depth, 0.6m and 1m.
Iron
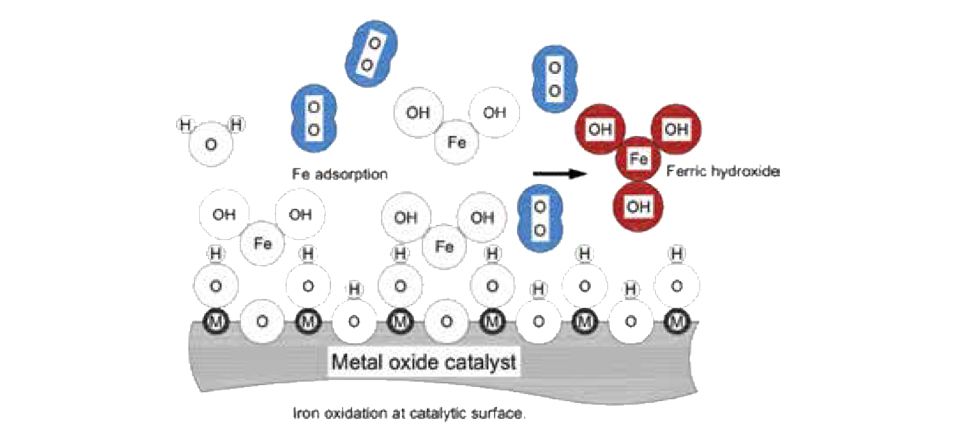
Iron (Fe) normally exists in 2 different states - Ferrous (+2) and Ferric (+3); Ferrous iron is commonly found as Ferrous Bicarbonate. DMI-Plus catalytic surface contains Manganese Oxide that oxidizes Ferrous Bicarbonate to Ferric Hydroxide. Insoluble Ferric Hydroxide will then be removed through media surface.
Iron
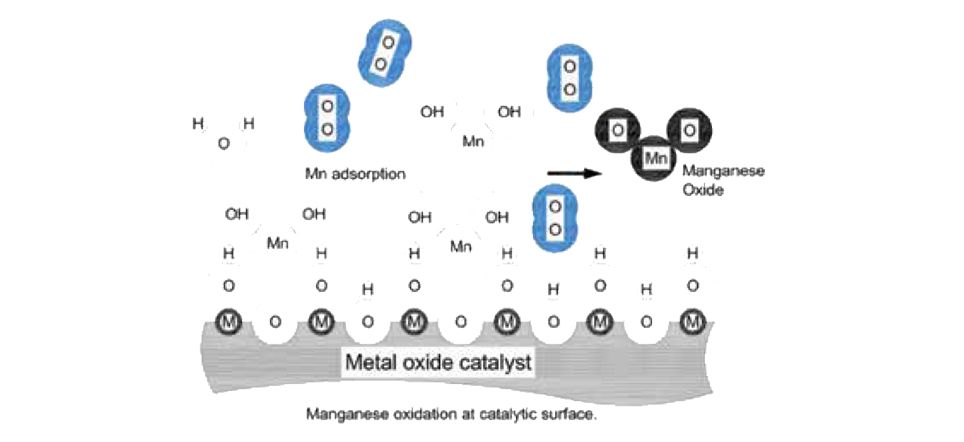
Catalytic surface of DMI-Plus oxidizes manganese to manganese hydroxide, in which it will be adsorbed and swapped with molecular oxygen in the lattice on catalytic surface.